

The model-view-controller (MVC) pattern divides an application into three components: A model, a view, and a controller. The application data and essential functionality are included in the model, which is the pattern's main building block. It governs the application's data and logic and is the dynamic data structure of the software. The logic that explains how the data is presented to a user is absent, though.
The view communicates with the user while displaying application data. It has access to the model's data, but it is unable to comprehend that data or how it may be changed.
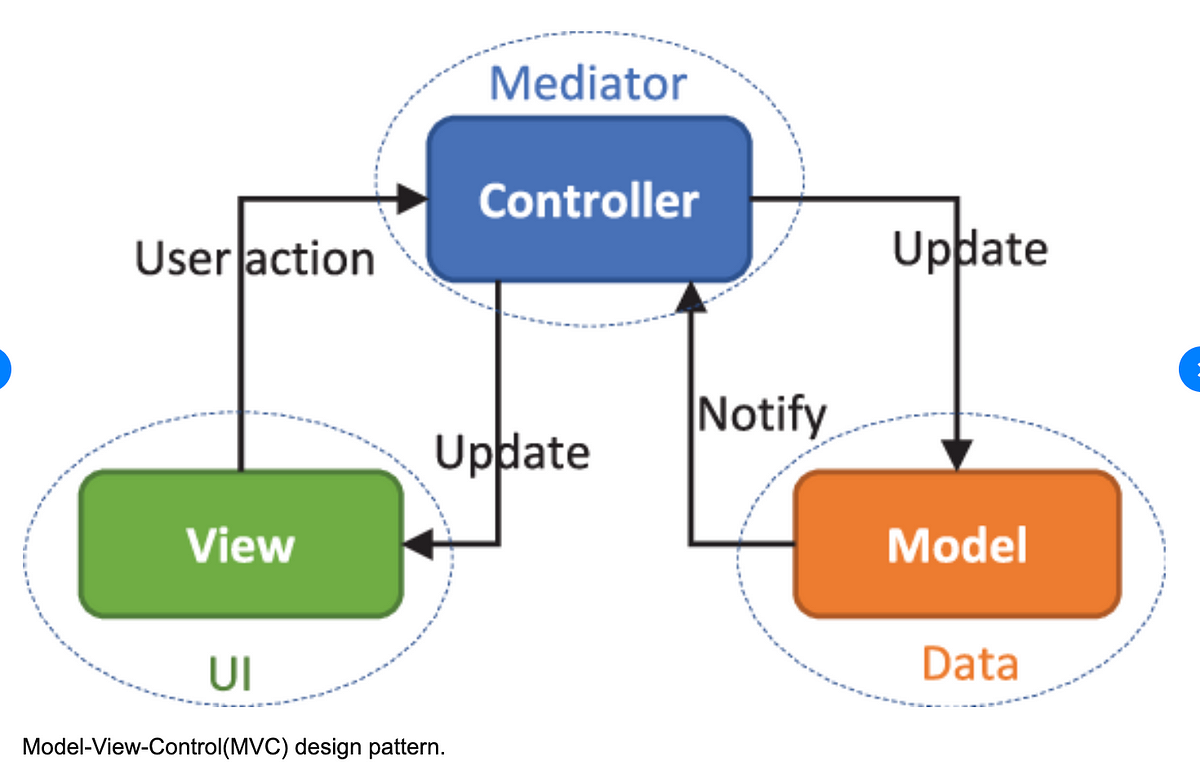 Image from medium.com.
Image from medium.com.
The controller acts as an interface between the model and the display and manages user input. It produces the necessary outputs after listening to external inputs from the view or a user. In order to produce suitable replies, the controller calls the model.
Here we are going to create a basic MVC web application that read and create data in database table. Firstly we create model for the application using Amazon DynamoDB. Then we create controller for the application with lambda fuction using Amazon Lambda and create API using Amazon API Gateway. At last, we create view or UI for our application using AWS Amplify.
So When we invoke our API Gateway API, API Gateway routes the request to your Lambda function. The Lambda function interacts with DynamoDB, and returns a response to API Gateway. API Gateway then returns a response to us.
You can use AWS free tier account to perform following steps.
For setting up DynamoDB for the application follow the guide on Setting Up DynamoDB by AWS.
To create a table in DynamoDB, sign in to the aws management console.
For detail guide on how to create database table in DynamoDB, follow the given link.
We will use AWS Lambda to create controller or lambda function for the application. This lambda function create, reads, update and delete items in DynamoDB. The function uses events from API Gateway to determine how to interact with DynamoDB.
To create lambda function:
const AWS = require(“aws-sdk”);
const dynamo = new AWS.DynamoDB.DocumentClient();
exports.handler = async (event, context) => {
let body;
let statusCode = 200;
const headers = {
“Content-Type”: “application/json”
};
try {
switch (event.httpMethod) {
case “DELETE”:
await dynamo
.delete({
TableName: “Student”,
Key: {
id: event.pathParameters.id
}
})
.promise();
body = `Deleted student ${event.pathParameters.id}`;
break;
case “GET”:
if (event.pathParameters != null) {
body = await dynamo
.get({
TableName: “Student”,
Key: {
id: event.pathParameters.id
}
})
.promise();
} else {
body = await dynamo.scan({ TableName: “Student” }).promise();
}
break;
case “POST”:
let requestJSON = JSON.parse(event.body);
await dynamo
.put({
TableName: “Student”,
Item: {
id: requestJSON.id,
name: requestJSON.name,
}
})
.promise();
body = `Added/Updated student ${requestJSON.id}`;
break;
default:
throw new Error(`Unsupported route: “${event.httpMethod}”`);
}
} catch (err) {
statusCode = 400;
body = err.message;
} finally {
body = JSON.stringify(body);
}
return {
statusCode,
body,
headers
};
};
The handler method is the method that will be executed when the lambda function is invoked. This function takes in two objects, event, and context. The event object contains all of the data sent from the event source and the context object provides several methods that allow you to interact with runtime information specific to that lambda function.
By using the event.httpMethod to differentiate the HTTP request, we can perform the create/update/delete and retrieve data from DynamoDB.
You can go through this link for detail information about creating, invoking, view logs and metrics.
All the requests and responses are handle through API. So, we create REST API in API Gateway. When the application receive HTTP request, API Gateway invokes the lambda function.
To create API in API Gateway:
For API GET by id and DELETE by id, we need to create another resource to specify path parameters.
To deploy the created API:
For detail information about creating APIs in API Gateway, you can follow this link.
To create frontend for our application, create a new file on text editor and paste the following code in it.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>MVC</title>
<script>
var saveStudent = (id,name)=>{
var myHeaders = new Headers();
// add content type header to object
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/json");
// using built in JSON utility package turn object to string and store in a variable
var raw = JSON.stringify({"id":id,"name":name});
// create a JSON object with parameters for API call and store in a variable
var requestOptions = {
method: 'POST',
headers: myHeaders,
body: raw,
redirect: 'follow'
};
// make API call with parameters and use promises to get response
fetch("YOUR-API-INVOKE-URL", requestOptions)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => alert(JSON.parse(result).body))
.catch(error => console.log('error', error));
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<label>Student ID :</label>
<input type="text" id="id">
<label>Student Name :</label>
<input type="text" id="name">
<!-- set button onClick method to call function we defined passing input values as parameters -->
<button type="button" onclick="saveStudent(document.getElementById('id').value,document.getElementById('name').value)">Save</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Group ID: 11522-23-23 | Project ID: 2023-S1-40